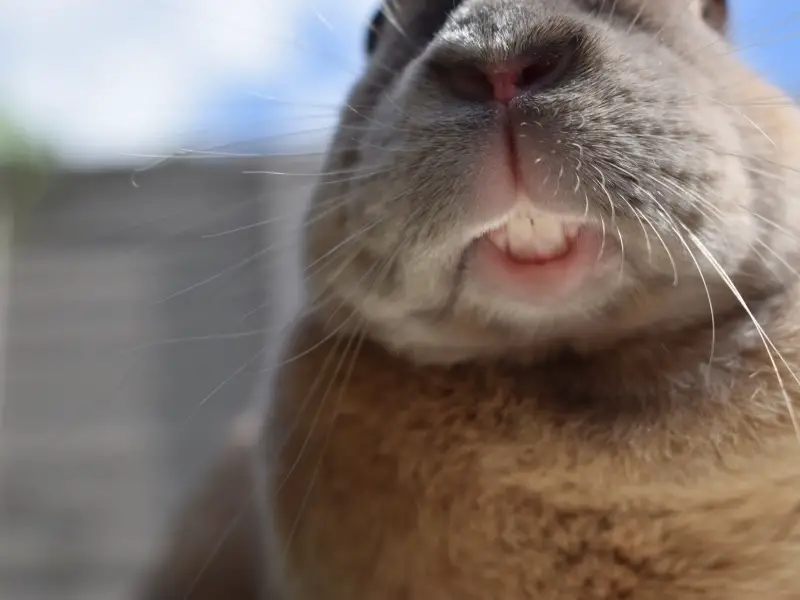
Rabbits are herbivores which means that they only eat a plant-based diet that mainly consists of vegetables and grasses. To accommodate their diet and lifestyle rabbits are born with open rooted teeth that continue to grow throughout their lives.
But how many teeth do rabbits have? Rabbits have 28 teeth. They have 2 lower and 2 upper incisors and 2 peg teeth that are right behind the top incisor teeth. In addition, rabbits also have 22 premolars and molars that they use to grind their food. There are 6 upper premolars, 4 lower premolars, 6 upper molars, and 6 lower molars.
In this article, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about rabbit teeth and common dental problems your pet rabbit might face. Keep on reading to find out more!
Do Rabbits Lose Their Teeth?
Just like humans, rabbits are diphyodont which means that they have two successive sets of teeth. The initial deciduous set of teeth will fall out and be replaced by the permanent set of teeth.
Baby rabbits, just like human babies, aren’t born with a set of teeth. Instead, baby rabbits, also known as kits, grow their first set of teeth when they are between 19 and 21 days old.
Although adult rabbits end up having 28 permanent teeth, baby rabbits start with only 16 milk or deciduous teeth. Most baby rabbits lose their 16 milk teeth when they are a few months old at which time their permanent teeth start to grow.
Rabbit Teeth Diseases
As mentioned previously, rabbits have open-rooted teeth, meaning that they are constantly growing throughout a rabbit’s life. Since their teeth continue to grow, the upper teeth must meet the lower teeth in the middle to allow for proper wearing of tooth surfaces.
Malocclusion is the most common dental problem rabbits face, and it happens when two teeth don’t meet in the middle which leads to asymmetrical wear (source). Improper wear can happen with incisor teeth or cheek teeth and can lead to more serious health problems.
Malocclusion can result in the abnormal growth of the front teeth and create sharp edges, spurs, or points on molars. These razor-sharp points may cut and badly injure the tongue, cheeks, or gums when the rabbit is chewing.
But that’s not all! Overgrown molars can form a bridge and trap a rabbit’s tongue. It’s also possible for molars to hit each other in the back of the mouth, therefore not allowing the mouth to close completely and preventing the incisors from meeting properly.
Things can get even worse as the overgrown upper and lower molars in the back of the mouth hit each other every time the rabbit chews or tries to close its mouth. As these teeth aren’t worn down they can become impacted in the upper and lower jaw, which can be extremely painful for a rabbit.
Malocclusion of the incisors will sometimes cause these big teeth to grow at an angle from each other, protrude from the mouth, curl back, curl sideways, or grow in many other bizarre ways.
Keep in mind that a rabbit’s teeth usually grow at a rate of 1 centimeter each month. And in a case of malocclusion, an incisor can grow around 1 millimeter per day (source).
Considering how fast a rabbit’s teeth grow, most dental problems become quite obvious early on. This means that you’ll have enough time to take your rabbit to your vet before things become more serious.
The most common signs and symptoms of teeth disease in rabbits are:
- Overgrown, deformed, or broken front teeth
- A rash around the eyes, weepy and protruded eyes
- Drool around the mouth
- Swelling around the face
- Weight loss
- A runny nose, snuffling or snoring
- Poor self-grooming
- Dirty bottom with soft droppings left on the fur
- Teeth grinding
- Diarrhea
- Behavioral changes such as increased irritability and grumpiness
In severe cases, a rabbit might stop eating completely, which is an emergency in itself. If this happens, take your rabbit to the vet right away otherwise, you risk losing your pet.
How Many Permanent Teeth Do Rabbits Have?
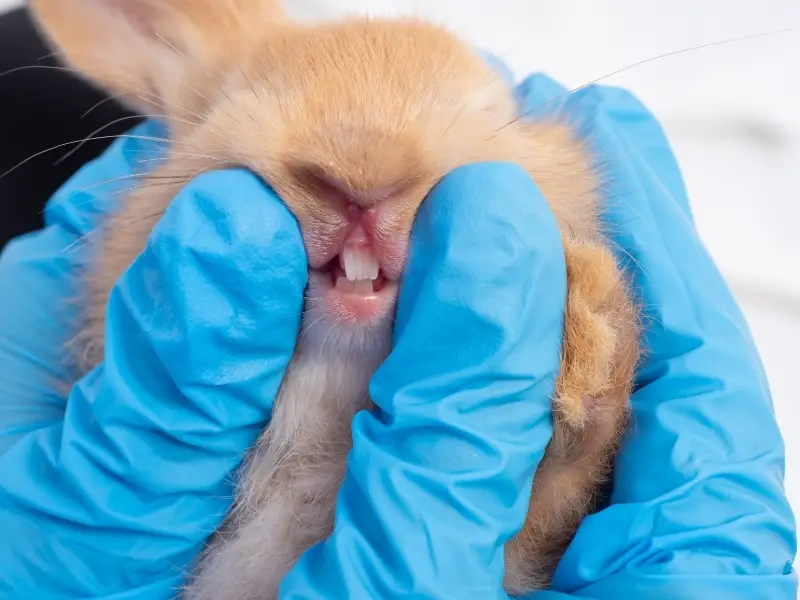
Rabbits have 28 permanent (secondary) teeth. Since they are herbivores, rabbits don’t have canine teeth like cats, dogs, ferrets, and hedgehogs.
When it comes to adult or permanent teeth, all rabbits have incisor and cheek teeth. Incisors are the big front teeth, and the cheek teeth include both the premolars and molars.
Expect to see 4 incisors, 2 in the upper jaw, and 2 in the lower jaw. Behind the top incisor teeth, adult rabbits have two smaller, peg-like teeth called auxiliary incisors or peg teeth.
Additionally, rabbits also have cheek teeth that they use for grinding their food. Each side has 6 teeth on the top and 5 teeth on the bottom, or to put it simply 22 premolars and molars.
What Are the Front Teeth of a Rabbit Called?
A rabbit’s big, front teeth are called incisors. All rabbits have 2 upper incisors and 2 lower incisors that continue to grow throughout their lives.
But that’s not all. Tucked behind the large upper incisors are the two smaller auxiliary incisors that are also known as peg teeth. The smaller peg incisors have a broader curvature and are roughly half as long as the bigger front incisor.
Conclusion
Just like people, rabbits have two successive sets of teeth. Once baby rabbits lose their milk teeth, the second permanent set grows and full-grown rabbits end up having 28 adult teeth.
The most important thing to remember about rabbit teeth though is that they continue to grow throughout a rabbit’s life. While you won’t have to brush or floss your bunny’s teeth to keep them healthy, you’ll need to ensure that they are worn down.
Feeding a rabbit-appropriate diet that consists of 70% hay is the best way to help your furry pet file its teeth naturally and prevent painful malocclusions.
Related Articles:

